Introduction
Patient retention is a critical aspect of clinical research, yet it poses numerous challenges that can impact the validity and reliability of study outcomes. This article explores the multifaceted challenges associated with patient retention in clinical research, delves into the reasons why patients leave studies prematurely, and presents innovative solutions, including the utilisation of software tools. Insights from key opinion leaders (KOLs) in the field are integrated to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex issue.
Key Idea
Patient retention is fundamental to the success of clinical research endeavors, as high dropout rates can compromise study integrity, prolong timelines, and inflate costs. Despite its importance, patient retention remains a persistent challenge in clinical trials across various therapeutic areas. Understanding the underlying reasons for patient attrition and implementing effective strategies to address these challenges are paramount for advancing clinical research.
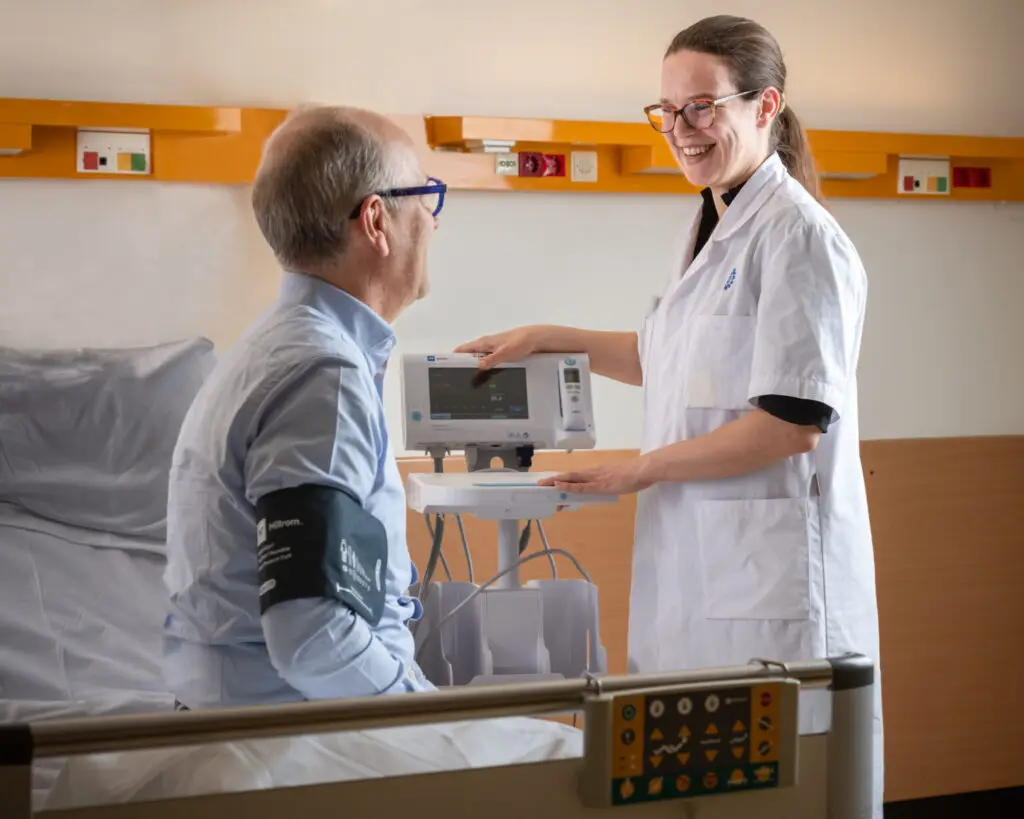

Key Challenges of Patient Retention
1. Participant Engagement
Sustaining participants’ interest and commitment throughout the trial can be challenging due to factors such as study burden, lack of motivation, and competing priorities.
2. Logistical Hurdles
Practical barriers such as transportation difficulties, scheduling conflicts, and financial constraints may impede participants’ ability to adhere to study requirements.
3. Adverse Events and Side Effects
Unforeseen adverse events or intolerable side effects experienced by participants can lead to premature discontinuation of the study.
4. Communication and Support
Inadequate communication channels and insufficient support from research staff can contribute to participant dissatisfaction and attrition.
Reasons for Patient Attrition
1. Perceived Study Burden
Participants may feel overwhelmed by the demands of the study protocol, including frequent clinic visits, complex procedures, and lengthy questionnaires.
2. Unforeseen Adverse Events
The occurrence of unexpected adverse events or side effects can prompt participants to discontinue their involvement in the trial out of concern for their safety and well-being.
3. Lack of Engagement
Participants may lose interest or motivation in the study due to a perceived lack of personal benefit, minimal interaction with study staff, or insufficient communication.
4. Logistical Challenges
Practical barriers such as transportation issues, childcare responsibilities, or work commitments may hinder participants’ ability to adhere to study requirements.
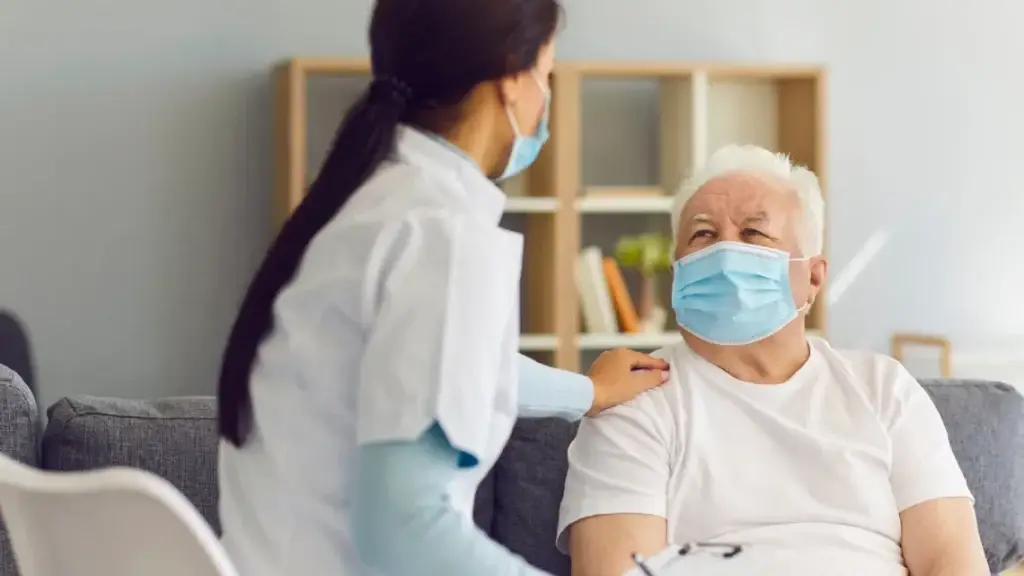

Key solutions to Enhance Patient Retention
1. Implement Patient-Centric Strategies
Designing patient-centric protocols that prioritise participant convenience, minimise study burden, and incorporate patient feedback can enhance engagement and retention.
2. Utilise Technology Solutions
Leveraging software tools such as electronic data capture (EDC) systems, remote monitoring platforms, and mobile health (mHealth) applications can streamline study procedures, facilitate real-time communication, and enhance participant engagement.
3. Enhance Communication and Support
Establishing clear channels of communication, providing personalised support, and fostering a supportive study environment can promote participant retention and satisfaction.
4. Offer Incentives and Recognition
Providing incentives such as financial compensation, travel reimbursements, or tokens of appreciation can incentivise participants to remain engaged in the study and feel valued for their contributions.

Key Opinion
“One of the buzz phrases of recent times in the clinical trials industry, patient engagement is increasingly being seen as a ‘must have’ rather than a ‘nice to have’.
From the earliest stages of trial protocol development, right through to sharing trial results and beyond, including patients in the process is becoming widely regarded as an essential element in ensuring a trial’s success. (Indeed, it seems highly likely that having patient involvement at every stage will be mandated in the near future – possibly in Europe first, then the US and rest of the world).
The benefits of engaging with patients stretch far beyond simply improving results for clinical trials, but from a patient recruitment perspective, it’s clear that having input from the people who will be participating in the trial can help reduce the burden placed on them. Thus leading to higher recruitment rates and increased retention during the trial’s lifespan.“
Excerpt from: 27 Ways to Recruit Patients for Clinical Trials
by Ross Jackson

Conclusion
Patient retention is a multifaceted challenge in clinical research, influenced by various factors ranging from participant engagement to logistical barriers. By understanding the reasons for patient attrition and implementing tailored solutions, including the utilisation of software tools and insights from key opinion leaders, researchers can enhance retention rates, optimise study outcomes, and ultimately advance the field of clinical research.



