Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of clinical research, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges. From expediting trial processes to enhancing patient identification, developing trial protocols, and identifying optimal trial sites, AI is revolutionising the way researchers conduct clinical studies.
In this article, we will explore the top uses of AI in clinical research, providing definitions and real-world use cases for each key area.
A recent poll unveiled intriguing results, showcasing the preferences of over 16,000 life science professionals regarding their anticipated implementation of AI in research this year. The responses, presented in percentages, shed light on the areas these professionals believe AI would be most beneficial for in their research endeavours.
The poll asked the question:
What do you want to start using AI for in 2024?
With the 4 options being:
A. Develop Trial Protocols
B. Identify Trial Sites
C. Streamline Trial Processes
D. Identify Prospective Participants
This question was presented to a group of 288,418 Life Science Professionals, among whom 16,324 had the opportunity to respond during the week the poll was available. Of those, 180 completed the poll.
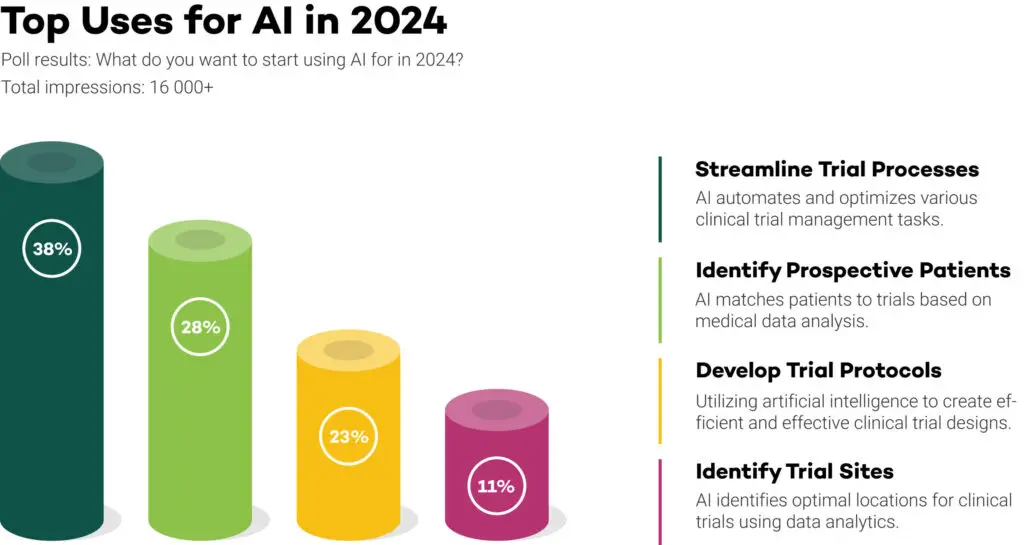
1. Streamlining Trial Processes 38.3%
Definition: Streamlining trial processes involves optimising the various steps and workflows in clinical trials, from participant recruitment to data analysis, to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Use Case: AI-powered data analytics can significantly accelerate the data collection and analysis phases of clinical trials. For example, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and trends in large datasets, allowing researchers to quickly analyse patient responses to treatments. This streamlines the trial process, reducing time and costs associated with data management.
Another excellent example is process automation, which diminishes the administrative burden on both researchers and patients. Utilising AI, tasks such as prescreening, visit scheduling and giving consent can be seamlessly be integrated into the trial process. For further information, click here: Visit Scheduling
2. Patient Identification 27.7%
Definition: Patient identification in clinical research refers to the process of selecting and recruiting suitable participants for a study based on specific criteria.
Use Case: AI algorithms can analyze electronic health records (EHRs) and other patient data to identify individuals who meet the criteria for a clinical trial. Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be employed to extract relevant information from unstructured data sources, such as physicians’ notes. This enables researchers to efficiently identify potential participants, improving recruitment rates and ensuring that the selected individuals align with the study’s requirements.
3. Develop Trial Protocols 22.7%
Definition: Developing trial protocols involves designing the detailed plan that outlines the objectives, methodology, and statistical considerations of a clinical trial.
Use Case: AI can assist in the design of trial protocols by analyzing historical data from similar studies and identifying potential pitfalls or opportunities for improvement. Machine learning models can predict patient outcomes based on various parameters, helping researchers tailor protocols to enhance the likelihood of success. This not only speeds up the protocol development process but also increases the likelihood of designing more effective and patient-centric studies.
4. Identify Trial Sites 11.1%
Definition: Identifying trial sites involves selecting suitable locations or institutions to conduct a clinical trial, considering factors such as patient demographics, infrastructure, and regulatory environment.
Use Case: AI can analyze a vast array of data, including geographical information, patient populations, and regulatory landscapes, to recommend optimal trial sites. By factoring in historical data on successful trial outcomes and patient recruitment rates in different locations, AI helps researchers make informed decisions about where to conduct their studies. This minimizes the risk of delays due to recruitment challenges and enhances the overall efficiency of the clinical trial.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in clinical research is ushering in a new era of efficiency and precision. By streamlining trial processes, improving patient identification, aiding in protocol development, and assisting in site selection, AI is enhancing the quality and speed of clinical research.
As the technology continues to advance, researchers can expect even more innovative applications that will further optimise the drug development pipeline and ultimately improve patient outcomes.



